New study identifies causal links behind the increase in hot and dry extremes in Central Europe
23.12.2024 - Hot extreme weather events in Central Europe are driven primarily by anomalous atmospheric patterns and soil water deficiency, a new study led by scientists from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research PIK shows. In contrast, dry extremes are mainly caused by atmospheric anomalies and soil moisture memory, and only marginally by temperature changes.
Read More
Leonie Wenz awarded Piers Sellers Prize 2024
25.06.2024 - The prestigious Piers Sellers Prize was awarded to Leonie Wenz. As one of two winners, the deputy head of Complexity Science at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) is being honoured for her world leading contribution to climate solutions, especially for her excellent research on the economic impacts of climate change.
Read More
Katja Frieler: Climate Impact Professorship at the University of Potsdam
05.06.2024 - Katja Frieler, head of the “Transformation Pathways” research department and the “Pathway-specific climate risks” division at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), took up the professorship for Climate Impacts at the University of Potsdam on April 1 this year.
Read More
Resonant planetary waves contributed to Pacific Northwest Heat Dome event of 2021
17.01.2024 - Recent decades have witnessed unprecedented heat waves with severe repercussions for human society. However, the causes for the extremity of some of these heat events are not yet understood. Researchers from the University of Pennsylvania and the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) now show, that the severe 'heat dome' incident in the north-western region of the US in 2021 was partly caused by the quasi-resonant amplification of planetary waves, a theory originally developed by the late renowned PIK scientist Vladimir Petoukhov. Published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences PNAS today, the findings hold the potential for more skillful predictions of potentially devastating future weather extremes.
Read More
CO2 emissions at record high in 2023
05.12.2023 - Global carbon dioxide emissions from fossil fuel use will amount to 36.8 billion tonnes in 2023, a record high that exceeds the 2022 level by 1.1% - the latest Global Carbon Budget report finds. This is a long way off the significant reductions that are needed to reach the Paris Agreement climate goals.
Read More
A fifth higher: Tropical cyclones substantially raise the Social Cost of Carbon
11/23/2023 - Extreme events like tropical cyclones have immediate impacts, but also long-term implications for societies. A new study published in the journal Nature Communications now finds: Accounting for the long-term impacts of these storms raises the global Social Cost of Carbon by more than 20 percent, compared to the estimates currently used for policy evaluations. This increase is mainly driven by the projected rise of tropical-cyclone damages to the major economies of India, USA, China, Taiwan, and Japan under global warming.
Read More
On the DWD's Summer Report 2023: In the midst of climate change
08/30/2023 - The German Weather Service (Deutscher Wetterdienst, DWD) has presented its 2023 summer report. PIK researcher Fred Hattermann comments: "This year's precipitation cannot compensate for the precipitation deficit that has accumulated over the past years."
Read More
Climate extremes hit stressed economies even harder
08/30/2023 - Economies already under stress respond more strongly to weather events like heat waves, river floods and tropical cyclones, a new study shows. A global economic crisis as during the Covid-19 pandemic strongly amplifies the price increases private households experience from the impacts of weather extremes, a team of researchers from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) finds. The price impacts tripled in China, doubled in the United States and increased by a third in the European Union.
Read More
Six decades and more than 1600 regions worldwide: New database on economic development and climate change
07/03/2023 - A new Database Of Sub-national Economic Output (DOSE) for the first time provides sub-national economic data for six decades and more than 1600 regions worldwide matched with climate observations. Developed by experts of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) and the Mercator Research Institute on Global Commons and Climate Change (MCC) the database aims to o better understand the implications of global warming on regional economic development and the true costs of climate change.
Read More
Less predictable rainfall important for Maya decline
03/17/2023 - Reduced predictability of seasonal rainfall might have played an important role in the disintegration of Classic Maya societies about 1100 years ago. That is the result of a new study of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) and Potsdam University. The research team studied variations in stable isotope signatures from a stalagmite that was collected in a cave near Uxbenka/Belize, an important archaeological site in the former heartland of the Maya. The carbon and oxygen isotope ratios are sensitive recorders of local and regional rainfall dynamics.
Read More
Earlier, higher, smaller: Climate change alters glacial lake outburst floods
02/16/2023 - Due to global warming, flood-like water outbursts from ice-dammed glacial lakes worldwide happen earlier in the year and originate from higher areas. This is shown on the basis of observation data since 1900 by a new study with the participation of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), which is published in the scientific journal Nature. At the same time, however, these so-called outbursts are also becoming smaller.
Read More
El Niño phenomenon: 2024 could be warmest year ever
02/03/2023 – With a likelihood of almost 90% the weather phenomenon "El Niño" will occur again in the Pacific region as early as this autumn. This may be accompanied by numerous extreme weather events, such as heavy rain in Peru and drought in Australia and Indonesia. As El Niño also increases global temperatures in the short term, there is a possibility that 2024 could be the warmest year since weather records began. This is what scientists from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), Justus Liebig University Giessen and two Beijing universities report in a recent analysis.
Read More
Climate risk insurance can effectively mitigate economic losses
01/04/2023 - Global warming is expected to lead to an accumulation of particularly intense hurricanes in the United States. This may substantially increase the economic losses caused by these storms. Better insurance could effectively mitigate the climate change-induced increase in economic losses. This is shown in a new study by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research examining the effectiveness of climate risk insurance in the US.
Read More
Early forests did not change the atmospheric CO2 level as much as previously thought
12/20/2022 - An international team of Earth scientists has discovered that the atmosphere contained far less CO2 than previously thought when forests emerged on our planet. The study published in Nature Communications alters a 30-year-old paradigm with important implications for understanding how land plants affect the climate.
Read More
Economic losses from hurricanes become too big to be offset by the US if warming continues
10/17/2022 - Hurricane damages can increase due to increasing global temperatures, caused by greenhouse gas emissions from fossil fuels. Computer simulations of regional economic sectors and supply chains in the US now show that the resulting economic losses can at some point not be nationally offset under unabated warming. If too many factories and the like are hit by the hurricane and stop working, other countries will have to step in to provide the supply of goods, according to the scientists who did the study. The hurricane impacts under global warming will thus give the US an economic disadvantage, the warmer the more.
Read More
Shifting Climate Zones: Sahel might get 50 % more rain by 2040
09/22/2022 - Climate change could turn one of Africa's driest regions into a very wet one by boosting the Monsoon circulation. New computer simulations show a significant future increase in seasonal rainfall in the Sahel under the current trend of global warming. A major increase in average rainfall might kick-in by 2040 already, which means that it is inevitable regardless of how future greenhouse gas emissions develop. Although crossing this new tipping point is potentially beneficial, it comes with substantial unknowns. The change could in fact be so big, it would be a major adaptation challenge for an already troubled region.
Read More
Extreme temperatures fuel online hate speech
09/08/2022 - Temperatures above or below a feel-good window of 12-21 degrees Celsius (54-70 °F) are linked to a marked rise in aggressive online behaviour across the USA, a new study finds. Analysing billions of tweets posted on the social media platform Twitter in the USA, researchers from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research found hate speech increasing across climate zones, income groups and belief systems for temperatures too hot or too cold. This indicates limits to adaptation to extreme temperatures, and sheds light on a yet underestimated societal impact of climate change: conflict in the digital sphere with implications for both societal cohesion and mental health.
Read More
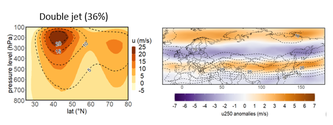
Increase in heatwaves in western Europe linked to changes in the jet stream
07/05/2022- Heatwaves over Europe have increased three to four times faster than in the rest of the northern mid-latitudes like e.g. the US or Canada, a new study finds. An international team of scientists looked at observational data from the past 40 years and showed, for the first time, that this rapid increase is linked to changes in the atmospheric circulation. Large-scale winds at 5 to 10km height, the so-called jet stream, are changing over Eurasia. Periods during which the jet stream is split into two branches – so called double jet states – have become longer lasting. These double jet states explain almost all of the upward trend in heatwaves in western Europe, and around 30 percent over the larger European domain.
Read More
PIK-Scientist Svenja Fluhrer awarded with Early Career Best Paper Award
06/03/2022 - Development economist Svenja Fluhrer was awarded with the prize "Ökonomie des Klimawandels - Early Career Best Paper Award" of the Federal Ministry of Education and Research. She received the award for her paper "Sitting in the same boat: Subjective well-being and social comparison after an extreme weather event", published in Ecological Economics.
Read More
Precise PIK forecasts of the beginning of the monsoon help farmers in India
05/17/2022 - For the 6. year in a row, PIK-scientist Elena Surovyatkina has predicted the onset of the Indian Summer Monsoon in Central India more than a month in advance. According to her forecast, the monsoon will begin between 14 and 18 June in Central India and Telangana and after 10 July reach Delhi. The unique forecast accounts for climate change effects, making it reliable to use for farming. It is the most awaited news for Indian farmers because the sowing and planting starts with the beginning of the rainy season.
Read More
Rainy days harm the economy
01/12/2022 - Economic growth goes down when the number of wet days and days with extreme rainfall go up, a team of Potsdam scientists finds. Rich countries are most severely affected and herein the manufacturing and service sectors, according to their study now published as cover story in the renowned science journal Nature. The data analysis of more than 1.500 regions over the past 40 years shows a clear connection and suggests that intensified daily rainfall driven by climate-change from burning oil and coal will harm the global economy.
Read More
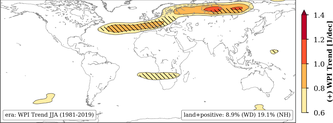
Too dry, too hot, or too wet: Increasing Weather Persistence in European Summer
12/06/2021 - Global warming makes long lasting weather situations in the Northern hemisphere‘s summer months more likely – which in turn leads to more extreme weather events, a novel analysis of atmospheric images and data finds. These events include heatwaves, droughts, intense rainy periods. Especially in Europe, but also in Russia, persistent weather patterns have increased in number and intensity over the last decades with weather extremes occurring simultaneously at different locations.
Read More
High impact climate events: Better adaptation through earlier prediction
11/16/2021 - The prediction of high impact climate phenomena can be substantially improved by a new mathematical approach that analyses the connectivity and patterns between geographical locations, scientists say in a new publication. This can potentially save thousands of lives and avoid billions in economic losses. Prediction times for events like El Niño, monsoons, droughts or extreme rainfall could be increased substantially, to a month or in some cases even a year in advance, depending on the type of the event. The new framework can thus become key for improving adaptation to the global warming crisis.
Read More
The Ripple Factor: Economic losses from weather extremes can amplify each other across the world
27/10/2021 - Weather extremes can cause economic ripples along our supply chains. If they occur at roughly the same time the ripples start interacting and can amplify even if they occur at completely different places around the world, a new study shows. The resulting economic losses are greater than the sum of the initial events, the researchers find in computer simulations of the global economic network. Rich economies are affected much stronger than poor ones, according to the calculations. Currently, weather extremes around the world are increasing due to greenhouse gas emissions from burning fossil fuels. If they happen simultaneously or in quick succession even at different places on the planet, their economic repercussions can become much bigger than previously thought.
Read More
Hotter, wetter, drier: the science behind extreme weather events
10/22/2021 - Extreme weather events are on the rise. Are these events connected? Are they becoming more likely with global warming? In the new episode of the podcast ‘Sustain Ability. The Potsdam Dialogues - Science for a Safe Tomorrow’, experts Friederike Otto and Stefan Rahmstorf give insight into their latest research.
Read More
Unprecedented rise of heat and rainfall extremes in observational data
10/7/2021 - A 90-fold increase in the frequency of monthly heat extremes in the past ten years compared to 1951-1980 has been found by scientists in observation data. Their analysis reveals that so-called 3-sigma heat events, which deviate strongly from what is normal in a given region, now on average affect about 9 percent of all land area at any time. Record daily rainfall events also increased in a non-linear way – on average, 1 in 4 rainfall records in the last decade can be attributed to climate change. Already today, extreme events linked to human-caused climate change are at unprecedented levels, the scientists say, and they must be expected to increase further.
Read More
Reducing tropical cyclone impacts: The double benefit of climate protection through both limiting and delaying global warming
09/27/2021 - Increasing global warming from currently one to two degrees Celsius by mid-century might lead to about 25 percent more people put at risk by tropical cyclones, a new study finds. Already today, hurricanes and typhoons are among the most destructive natural disasters worldwide and potentially threaten about 150 million people each year. Adding to climate change, population growth further drives tropical cyclone exposure, especially in coastal areas of East African countries and the United States. Considering the joint impact of climate change and population growth provides an untapped potential to protect a changing world population.
Read More
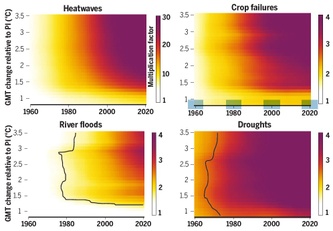
Today’s children to experience two to seven times more extremes than their grandparents
09/27/2021 - Today’s children will be hit much harder by climate extremes than today’s adults, researchers show in the leading journal Science. During their lifetime, a child born in 2021 will experience on average twice as many wildfires, between two and three times more droughts, almost three times more river floods and crop failures, and seven times more heatwaves compared to a person who’s for instance 60 years old today, the researchers find based on data from the Inter-sectoral Impact Model Intercomparison Project (ISIMIP). This is under a scenario of current greenhouse gas emission reduction pledges by governments which will be a topic at the upcoming world climate summit COP26 in Glasgow.
Read More
PIK expertise on extreme rainfall and flooding
07/16/2021 - The heavy rains and thunderstorms in parts of North Rhine-Westphalia and Rhineland-Palatinate during the past days have led to massive flooding of villages and entire areas. Meanwhile, towards the rivers Oder and Neiße, extreme heat prevailed at more than 30 degrees Celsius. Where these extraordinary weather conditions stem from and their connection with climate change, many national and international media wanted to know from PIK researchers. Here is a small excerpt from the coverage.
Read More
Winter weather, a polar front – and areas of drought: PIK's assessment of the current weather situation.
02/12/2021 - In January and February of 2021, parts of Europe, America and also Germany have experienced partly extreme winter weather. Nevertheless, there are widespread large areas of drought especially in Germany - PIK researchers Stephan Rahmstorf and Fred Hattermann on current climate-related weather changes.
Read More