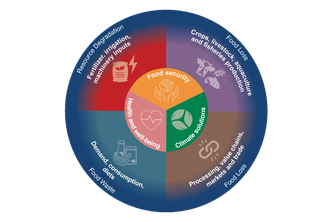
From artificial meat to fine-tuning photosynthesis: Food System Innovation – and how to get there
19/05/2020 - Food production has always shaped the lives of humans and the surface of the Earth. Be it plough or refrigerator, time and again innovations have transformed the ways we grow, process, and consume food over the last millennia. Today, with almost 40 per cent of all land on Earth used for food production, the food system massively impacts climate and environment – from nitrogen flows to water use, from biodiversity to greenhouse gas emissions. In a new study published in the journal NatureFOOD, an international team of researchers has now assessed and categorised key innovations with a potential to transform the food system, from artificial meat or seafood to biofortified crops or improved climate forecasts – and established what is most needed to make them succeed.
Read More
From forests to peatlands: once lost, ecosystem carbon stores might not be recoverable in time
01/04/2020 - Huge amounts of carbon are stored in ecosystems like peatlands, mangroves, old-growth forests and marshes, which play a crucial role for our Earth system. Once released due to land use changes like the conversion to agriculture, this carbon could be not be recoverable within time to avoid global warming beyond 1,5 degrees Celsius, a new study led by Conservation International shows. Johan Rockström, Director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, is one of the authors. These land areas should be particularly protected, the researchers argue in the journal Nature Climate Change.
Read More
Regional nuclear war a risk for global food security
16/03/2020 - Even a limited nuclear war could have dangerous effects far beyond the region that is fatally hit. It would result in global cooling that substantially reduces agricultural production in the world’s main breadbasket regions, from the US, to Europe, Russia, and China. The particular effect on food security worldwide including trade responses has now for the first time been revealed by an international team of scientists in a study based on advanced computer simulations. The sudden temperature reduction would lead to a food system shock unprecedented in documented history. It would not undo long-term climate change from fossil fuels use, though – after about a decade of cooling, global warming would surge again.
Read More
Managing forests in the 21st century: Experts gather at PIK
06/03/2020 - Forests all over Europe feel the pressure from ongoing climate change, yet at the same time provide a wide range of resources to mitigate and to adapt to global warming. Smartly targeted management of forest is thus key, finds an international gathering of leading experts hosted by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research this week. More than 100 scientists from institutions ranging from German National Park Berchtesgarden to US Oregon State University and Russian Higher School of Economics participated in three days of intense discussions and a field trip, more than 30 additional participants joined via videolink.
Read More
Ricarda Winkelmann departs on “Expedition Anthropocene“ on Mount Chimborazo, Ecuador
24/02/2020 – Humans are the defining geological force shaping Earth in our current epoch that has been named the Anthropocene. Across disciplinary boundaries, six members of the 'Junge Akademie', the academy of prominent young scientists and artists from German speaking backgrounds, have departed on an expedition on tracing some of human’s impact onto the environment. 200 years after Alexander von Humboldt, they will climb the Ecuadorian volcano Chimborazo in search of humanity’s footprint in different altitudes and vegetation zones. Besides PIK’s Ricarda Winkelmann, a mathematician glaciologist, the scientists involved come from a great variety of disciplinary backgrounds: biology, chemistry, sound ecology, computer science, and medicine.
Read More
Focus on food to address climate change
18/02/2020 - Bringing together agricultural production, supply chains, and consumption: In a comment published in the new journal Nature Food researchers discuss a new global food system approach to climate change research. When these activities are considered together, they represent 21 to 37 percent of total human-caused greenhouse gas emissions, the authors note. This new approach also enables a fuller assessment of the vulnerability of the global food system to increasing droughts, intensifying heatwaves, heavier downpours, and exacerbated coastal flooding. Food system responses thus play a major role in both adapting to and mitigating climate change, the authors assert.
Read More
Buildings can become a global CO2 sink if made out of wood instead of cement and steel
A material revolution replacing cement and steel in urban construction by wood can have double benefits for climate stabilization, a new study shows. First, it can avoid greenhouse gas emissions from cement and steel production. Second, it can turn buildings into a carbon sink as they store the CO2 taken up from the air by trees that are harvested and used as engineered timber. However while the required amount of timber harvest is available in theory, such an upscaling would clearly need most careful, sustainable forest management and governance, the international team of authors stresses.
Read More
Rockström as one Voice of Science at Davos World Economic Forum
21/01/2020 – After a year of climate change making headlines, the global leaders’ meeting at the World Economic Forum in Davos, too, has climate change written in large letters on its programme. Johan Rockström, Director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research is one of the scientists present to make the voice of science heard.
Read More
Tipping mechanisms could spark profound societal change towards climate stabilization: new study
21/01/2020 - Limiting global warming to well below 2°C requires a decarbonized world by 2050 at the latest and a corresponding global transformation of the energy and land use systems of societies across the world. To achieve this goal of net-zero carbon by 2050 emissions need to be cut by half every decade from now on. An interdisciplinary team of researchers now explored tipping mechanisms that have the potential to spark rapid yet constructive societal changes towards climate stabilization and overall sustainability. These tipping elements and mechanisms could bring about a transition that is fast enough for meeting the targets of the Paris climate agreement. Published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) the scientists identify six socio-economic tipping elements and related interventions that could bring such a transition to a deep and rapid global decarbonization on its way.
Read More
Feeding the world without wrecking the planet is possible
20/01/2020 - Almost half of current food production is harmful to our planet – causing biodiversity loss, ecosystem degradation and water stress. But as world population continues to grow, can that last? A study led by researchers from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) now suggests a comprehensive solution package for feeding 10 billion people within our planet’s environmental boundaries. Supplying a sufficient and healthy diet for every person whilst keeping our biosphere largely intact will require no less than a technological and socio-cultural U-turn. It includes adopting radically different ways of farming, reduction of food waste, and dietary changes. The study's publication coincides with the World Economic Forum in Davos and the International Green Week in Berlin, the world's biggest food and agriculture fair.
Read More
Climate change, food and agriculture: PIK expertise at International Green Week in Berlin
20/01/2020 - Hundreds of thousands of people are currently exploring the International Green Week in Berlin, a leading global trade fair for agriculture and food with featuring more than 1800 exhibitors from 72 countries. According to the organizers, the International Green Week 2020 is focusing on climate change like never before, with numerous exhibitions and events. This year's trend topics include sustainability, resource conservation and environmentally friendly production processes. Experts from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) will also be present at events at the Green Week from 17-26 January.
Read More
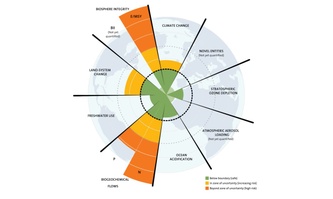
Planetary boundaries: Interactions in the Earth system amplify human impacts
16/12/2019 - What we do to one part of our Earth system does not just add to what we do to other parts – transgressing one planetary boundary can amplify human impacts on another one. For the first time, an international team of scientists now quantified some of the planetary-scale interactions in the Earth system. These biophysical interactions have in fact almost doubled direct human impacts on the nine planetary boundaries, from climate change to freshwater use. This insight can now be applied in policy design for safeguarding the livelihoods of generations to come.
Read More
Global food production at risk of simultaneous heat waves across breadbasket regions
09/12/2019 - Certain patterns in the jet stream encircling the Earth can bring simultaneous heatwaves to breadbasket regions responsible for up to a quarter of global food production. Particularly susceptible are Western North America, Western Europe, Western Russia and Ukraine. Extreme weather events of such extent can significantly harm food production and thus make prices soar. In recent years, major food price spikes were associated with social unrest.
Read More
Decarbonizing the power sector: renewable energy offers most benefits for health and environment
19/11/2019 - Electricity supply is one of the biggest CO2 emitters globally. To keep global warming well below 2°C, several paths lead to zero emissions in the energy sector, and each has its potential environmental impacts - such as air and water pollution, land-use or water demand. Using a first-time combination of multiple modelling systems, an international team of researchers led by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) has now quantified the actual benefits and downsides of three main roads to decarbonisation. They show that relying mainly on wind and solar would bring most co-benefits for the health of people and planet. Switching to carbon capture and storage in combination with fossil and biomass resources, in turn, is likely to convey significant environmental costs by devouring large areas at the cost of biodiversity, and by releasing pollutants to the environment.
Read More
Johan Rockström Chairs Newly Launched Earth Commission
19/09/2019 - The initiative of 20 globally renowned scientists on Earth Systems sets out to identify the concrete risks climate change brings for cities and firms. They aim to delineate the exact scientific borders of what our Planet can bear in terms of human-made climatic changes. Specifically, the commission will elaborate concrete tangible targets for cities and firms, thus scientifically underpinning tailored Goals for Land, Water, Oceans, and Biodiversity.
Read More
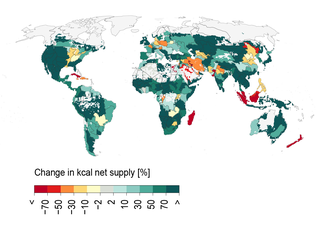
From avocados to apples: Producing food closer to cities could help reduce climate emissions
29.08.2019 - Millions of tons of groceries from agriculture are transported to our cities all around the globe every day to feed its dwellers. Produced anywhere in the world and transported as cargo on roads, rail or water from the farm gate into cities, this food transport is linked to a huge amount of CO2 emissions. Exploring options to reduce this “food-print”, a team of city researchers from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) now provides the first global analysis of the potential of local food production to feed hungry cities in present and future. As it turns out, a large number of urban residents in many parts of the world could be nourished by local agriculture. However, climate change might take that option off the table, if greenhouse gas emissions are not rapidly reduced.
Read More
Looking beyond the farm gate: New IPCC Special Report on Land Use and Climate Change
08/08/2019 – Almost three quarters of habitable land on earth are under human use – resulting in substantial impacts on our climate, a new report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) shows. Today, almost a quarter of human-made greenhouse gas emissions arise from agriculture, forestry and other land use. The latest IPCC Special Report investigates the current situation, possible future scenarios and potential solutions on how we can use land to feed ourselves, fuel economic growth and limit climate change risks. Two Potsdam scientists figure as lead authors of the chapter on food security and on the relations between land and climate.
Read More
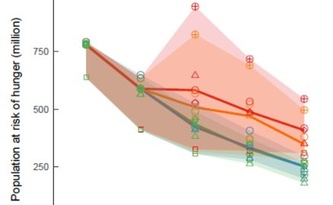
Climate mitigation can – and must – include policies to assure food security
13/05/2019 – Policies that aim at limiting dangerous climate change need to account for food security issues. For the first time, tradeoffs between climate mitigation and food security have now been analyzed in a so-called multi-model assessment: many different computer simulations dealing with the same issue. The costs for food-smart climate policies are around 0.2% of global economic output in 2050, an international team of scientists. However, carelessly designed climate policy could increase the number of people at risk of hunger, at least compared to a baseline scenario, according to the study now published in Nature Sustainability. Compared to today, the number of people at risk of hunger is likely to sink in all scenarios studied. Yet if no climate policy at all would be implemented, the resulting risks for crop failure due to droughts and floods might also lead to hunger and costs. Including these impacts of extreme events is a challenge for future research.
Read More
Amazon forest can be trained by higher rainfall variability – but may be no match for climate change
25.02.2019 - The Amazon rainforest has evolved over millions of years and even through ice ages. Yet today, human influences and global climate change put this huge ecosystem at risk of large-scale dieback – with major consequences for its capability as a global CO2 sink. New research published in Nature Geoscience now reveals a key player in shaping the resilience of the Amazon, and finds that regions with generally higher rainfall variability are more resilient to current and future climate disturbances. However, despite this 'training effect', the Amazon rainforest might not be able to keep up with the pace of ongoing climate change, the study shows.
Read More
New cookbook by Johan Rockström, now in German: "Eat Good" with healthy recipes for us and our planet
04/02/2019 - Unhealthy nutrition is one of the biggest causes of health risks worldwide and at the same time a risk to climate stability. What we eat can make a decisive contribution to our health and that of our planet. Healthy and sustainable recipes have now been presented by Johan Rockström, Director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and one of the authors of the recently published EAT Lancet report on healthy nutrition within the planetary boundaries. "Eat Good - The world-changing cookbook" the German cookbook is titled. The recipes ranging from breakfast to festive dinner are backed up by practical tips and background facts about food and its processing.
Read More
The living lab experiment "Climate-Neutral Living in Berlin" takes stock: Everyone can contribute to climate stabilization, but without politics it won’t succeed
31/01/2019 - "Climate-Neutral Living in Berlin" – for one year, more than 100 Berlin households have tried to shift to a more climate-friendly everyday life, from families with children, partners, flatmates to singles. In the living lab experiment headed by the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), households were reducing their climate footprint by an average of around 10 percent, even though they had, on average, already started the project 25 percent below the German average. The results of the project: in all sectors, from nutrition and consumption to electricity, heating and mobility, there is great potential for each and every one to reduce their CO2 emissions. But the experiment also shows where the limits of individual contributions to climate protection are, and where a political framework is necessary to set the stage for a more climate-friendly everyday life.
Read More
International Green Week: Agriculture expert Lotze-Campen speaks at several events
22/01/2019 - From agriculture and biodiversity to digital technologies in the agricultural sector to climate change and food: During and before the International Green Week (18-21 Jan), agricultural economist Hermann Lotze-Campen, head of research department "Climate Resilience - Climate Impacts and Adaptation" at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research, was invited as speaker at several events of various federal ministries in Berlin.
Read More
Lancet report: Healthy lives and a liveable planet for all require major changes in what we eat and how we produce it
17.01.2019 - Feeding a growing population of 10 billion by 2050 is possible if we shift towards a planetary health diet, a major new report by the EAT Lancet commission shows. International experts worked with the leading medical journal to develop the first comprehensive and detailed science based targets for improving our food system in a way that ensures healthy lives and a liveable planet for all. This includes doubling the amount of vegetables in what we eat every day, and halving red meat and sugar. Current diets are one of today's greatest causes for ill-health worldwide and in the same time threaten climate stability. Leading planetary boundaries researcher Johan Rockström, Director Designate of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research and former Director of the Stockholm Resilience Centre, is one of the report's lead authors.
Read More
Science to COP25: Must Knows for Climate Negotiators
06/12/2019 – The pace of contemporary rise in greenhouse gas concentrations is unprecedented in climate history over the past 66 million years and weather extremes are the “new normal,” according to some of the latest findings in climate science compiled in an easy-to-read guide for negotiators, policymakers, and media for the COP25 world climate summit. PIK Director Johan Rockström and colleagues from Future Earth and the Earth League today presented the “10 New Insights in Climate Science” report to UNFCCC’s Executive Secretary Patricia Espinosa at the meeting in the Spanish capital Madrid.
Read More
Ackerdemia wins KfW award 2018
19/10/2018 - The project of the former scientist of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), Christoph Schmitz, has been honoured with the special prize for Social Entrepreneurship in the nationwide corporate competition "KfW Award Gründen 2018". Ackerdemia aims at introducing children to a healthy diet through direct experiences on the field.
Read More
Manifesto by Wolfgang Lucht: "Das Wasser der Nachfolge"
05.10.2018 - We live in the Anthropocene, an era in which mankind as a global, geological force is changing the earth. Climate change, ocean acidification, extinction of species, deforestation and overfishing are just a few symptoms of human influence on our planet. "So what is the churches' opinion on the environmental question?" What do we say as Christians?", asks Wolfgang Lucht, Co-Chair of the Research Domain Earth System Analysis at the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK) in his manifesto "Das Wasser der Nachfolge". This chapter was published in the recently released German book "Life in the Anthropocene - Christian perspectives for a culture of sustainability" by oekom. His manifesto directly adresses the churches, whose commitment is vital for the necessary transformation to a socially and environmentally sustainable society.
Read More
Sustainable and healthy food to feed the world in 2050: Nature study
10/10/2018 - “Feeding a world population of 10 billion people is possible - yet only if we change the way we eat, and the way we produce food, our research shows. Greening the food sector or eating up our planet: this is what is on the menu today,” says Johan Rockström, Director Designate of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research. He’s one of the authors of a new study now published by an international team of scientists in the journal Nature.
Read More
Potsdam Summer School 2018: The skin of our planet
12/09/2018 - 42 outstanding young talents from 36 countries around the world will come together in Potsdam to discuss the interplay of dynamic processes on the Earth's surface. This year’s Potsdam Summer School, from the 10 to 19 September, is dealing with the skin of our planet, also featuring experts from the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK). In lectures, discussions and workshops with scientists from leading research institutes in Potsdam, but also on an excursion to the Spreewald Biosphere Reserve, international young talents from science, industry and the public sector will discuss highly topical research issues and strengthen international cooperation.
Read More
Flipping the switch: making use of carbon price dollars for health and education
07/16/2018 - While health systems, clean water and education are a plain given in many parts of the world, millions of people still do not have sufficient access to these basic public goods. In fact, carbon prices could make substantial financial resources available for succeeding with the global Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set by the United Nations, a team of scientists now finds. At the same time, carbon pricing could be a central contribution to meet global climate targets and limit global warming to well below 2°C until the end of the century.
Read More
New Report “The World in 2050”: Sustainable development experts meet in New York
07/10/2018 - From education and health to responsible consumption, a decarbonized energy-system, agriculture, sustainable cities and digitalization - six transformations are necessary to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) set by the United Nations, a new report by leading experts in the field finds. Published at the High-Level Political Forum on Sustainable Development (HLPF) in New York this week, the new report prepared by The World in 2050 (TWI2050) initiative outlines the key points that are necessary to bring the world on target to a sustainable future. More than 60 authors and 20 organizations were involved in the report, among them Johan Rockström, current Director of the Stockholm Resilience Centre and designated Director of the Potsdam Institute for Climate Impact Research (PIK), as well as PIK researchers Elmar Kriegler, Hermann Lotze-Campen and Alexander Popp.
Read More