"If we heat up Earth and destroy nature, this will directly threaten our prosperity and livelihoods, and the poorer people in our country and worldwide will be particularly hard hit," explains lead author Bjoern Soergel. "Climate impacts such as weather extremes or consequences of nature degradation increase risks for example to agriculture, affecting farmers' incomes, food prices, and ultimately everyone's nutrition and health."
Conversely, putting a price on CO2 emissions and phasing out climate-damaging fossil fuel subsidies can both reduce emissions, thus limiting warming, and generate government revenues. These revenues can be used to make direct cash transfers to people to compensate for rising energy and food prices; in Germany, for instance, this could lead to a net financial gain for the poorer half of the population. Especially in countries of the global South, carbon pricing revenues can also finance urgently needed investments in infrastructure, health care or education.
Further, if the right incentives were set in food and agricultural policy, for instance towards a diet with less meat, less land consumption, lower emissions and less use of artificial fertilizers, this could ultimately benefit everyone: healthy people on a healthy planet.
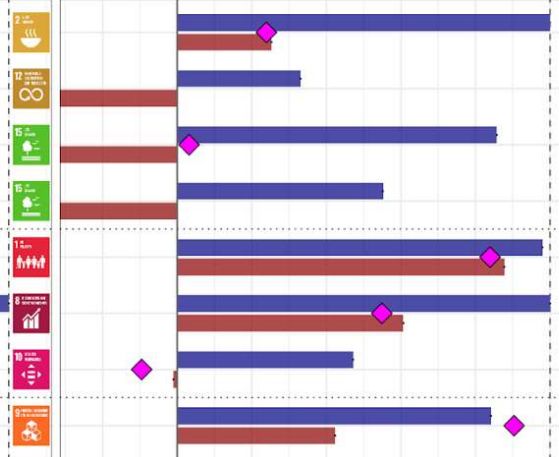
Carbon pricing could reduce emissions and generate revenue needed to achieve the UN Sustainable Development Goals
"None of this is simple," emphasizes co-author Ottmar Edenhofer, director of PIK. "Fifty years after the UN Stockholm Summit on the Human Environment, the challenges of equitable sustainable development are more pronounced than ever. However, our model calculations also show the opportunities of strong and comprehensive climate, environmental and social policies. In some countries, for instance India, carbon pricing could raise a good portion of the funds needed to achieve the UN Sustainable Development Goals. On the other hand, many African countries in particular need billions of euros in support of this."
"We have to acknowledge that there is no free lunch," Edenhofer concludes. "Either we continue paying for the damage to climate and nature, and ultimately for human suffering. Or we start to pay for the solutions."
Publication:
Bjoern Soergel, Elmar Kriegler, Christoph Bertram, Michael Crawford, Laura Delsa, Max Franks, Florian Humpenöder, Debbora Leip, Kai Lessmann, Alexander Popp, Nicolas Taconet, Isabelle Weindl, and Ottmar Edenhofer (2022): Joint implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals, climate change mitigation and biosphere protection: Policy options for tackling multiple crises simultaneously. Policy Paper [DOI:10.48485/pik.2022.003]
Contact:
PIK press office
Phone: +49 331 288 25 07
E-Mail: press@pik-potsdam.de
Twitter: @PIK_Climate
www.pik-potsdam.de





