World-class science at PIK on how to tackle global challenges needs to be complemented by selected in-depth case studies at the regional scale. PIK research should be relevant for Brandenburg, our host location, and Germany, by assessing, for example, transformation pathways for the Lausitz region. But climate impacts, adaptation and mitigation also need to be better understood in selected key regions on other continents, because many developing countries in Sub-Saharan Africa, Asia, and Latin America will be hit especially hard.
We conduct cross-sectoral impact assessments of specific regional climate risks and adaptation solutions, closely integrating methods from hydrology, agricultural and forest sciences, public health, and economics. Systematic and comparative regional case studies will feed into innovative climate services, and this knowledge transfer to regional decision-makers will contribute to the implementation of the Sustainable Development Goals.
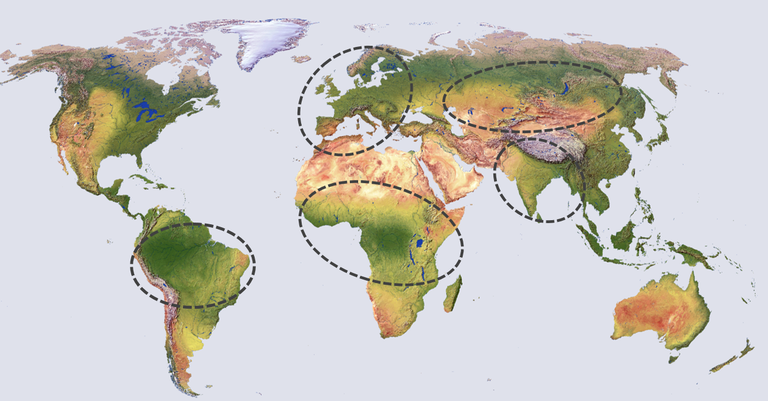
Peru, Brazil & Bolivia
Disruptive weather phenomena like El Niño have the power to jeopardize food and water security as the basis of a resilient development on a national, regional and local level. Cross-sectoral planning based on seasonal forecasts is vital to harmonise adaptation and mitigation options for a higher resilience towards climate variability in the future.
West & East Africa
In the face of climate change, sub-Saharan Africa has to cope with diverse challenges. A fast growing population, increasing demands for resources and arising conflicts need to be managed in a sustainable way guided through the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). Especially food, water and energy security are crucial for a resilient development pathway.
Europe
The impacts of climate change in Europe require different options of adaptation and mitigation to support climate-neutral and risk-adjusted development. Assessments of risks and the cost of climate change impacts go hand in hand with modelling scenarios for decarbonisation pathways and management options for viticulture and forest on the continent across national borders.
Germany
Climate change affects all sectors of society. Therefore, it is important to factor in future impacts into today’s planning processes to avoid severe negative consequences. Precautionary measures reach from developing a climate-neutral pathway for a region over a transformation of the tourism sector to the sustainable intensification of the bioeconomy. Altogether, adaptation options need to be explored, funded and implemented.
Central Asia & Russia
The Central Asian and Russian development highly depends on water resources and dry steppes cover a vast area. Although some of those steppes function as the Eurasian breadbasket, many of these lands have been abandoned after the collapse of the Soviet Union with strong impacts on land-use, agricultural production, water availability and the storage of GHGs. To cope with these challenges, capacity building and implementing risk transfer mechanism can support a resilient economic development.
South Asia & India
In a region with seasonally occurring extreme weather events, adaptation of all sectors to these circumstances was and is key to development and stability. Due to a changing climate, a solid database as the foundation for decision-making, investors and insurances helps to adapt and buffer the impacts of extreme events and raise awareness for the relevance of adaptation and mitigation.





